The Difference Between Tennis Elbow and Golfer’s Elbow
February 12, 2018Anup Patel, MD, MBA Named University of Florida Outstanding Young Alumus
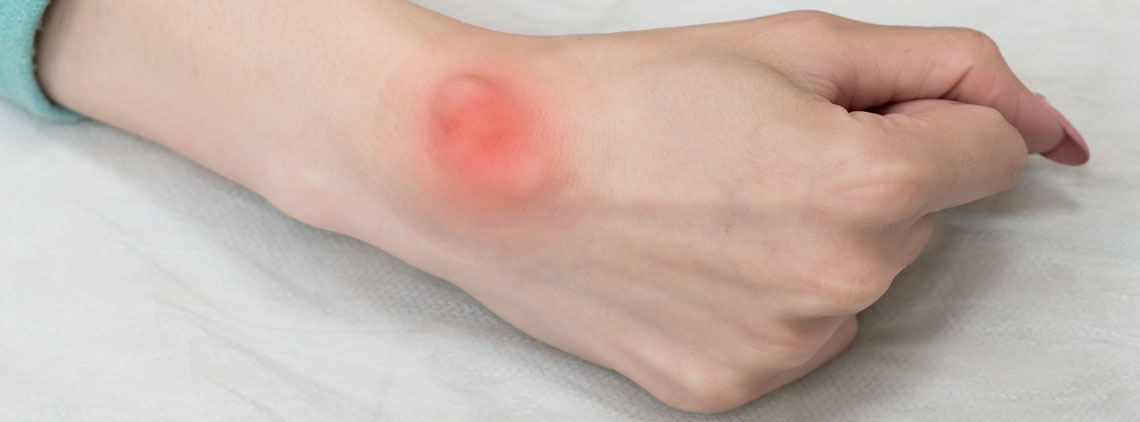
April 9, 2019A ganglion cyst is a common condition within the hand and wrist. These cysts are noncancerous and appear as a lump or bump underneath the skin. A ganglion cyst is commonly located on the top of the wrist, the palm side of the wrist, the base of the finger, and the top of the finger (near the nail bed).
Symptoms
Ganglion cysts can be categorized by location, size, and pain. They usually surface from the fluid-filled areas on the ligaments or between the bones. These cysts most commonly occur on the wrist or hand.
The size of the cyst can fluctuate. The fluid within the cyst can thicken over time causing it to become firm and progressively larger in size.
Often times a cyst is painless. If there is discomfort or pain, it could be due to pressure from the cyst pressing on a nerve. Discomfort from a cyst can include tingling, numbness, and muscle weakness.

Cause
The cause of a ganglion cyst is unknown. These cysts usually grow out of a joint or a tendon. Cysts may form when there is joint or tendon irritation. The fluid-filled in the cyst is harmless and can occur in patients of all ages.
Diagnosis
You should visit a physician if you have a noticeable lump or bump that causes pain or discomfort. During your appointment, the doctor may perform a physical exam to evaluate pain or discomfort. Your doctor may also recommend an X-ray, ultrasound, or magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) to check for possible other cyst causes, such as arthritis or a tumor.
Treatment
If the ganglion cyst is painless, treatment may not be required. If the cyst begins to cause pain or discomfort, or if it limits activity, your doctor may recommend these treatment options:
- Immobilization by wearing a splint
- Anti-inflammatory medication to decrease pain
- An aspiration to remove the fluid located in the cyst
If symptoms continue to occur after using the treatment options listed above, surgery may be recommended. During surgery, the cyst is removed, along with the stalk that attaches it to the joint or tendon. Even after surgery, a cyst may reappear.
The ganglion cyst should not be manipulated, “popped,” or punctured in any way without the guidance and care of a doctor. Doing so can lead to infection and is unlikely to be an effective solution.
If you have questions about a ganglion cyst, or other hand and wrist conditions, contact our office by clicking the links below:
CALL: (407) 841 – 2100 • TEXT: (844) 809-1082
You can also request an appointment by clicking the button below: